3/C. Credit: Wang Jialu” width=”800″ height=”530″/>
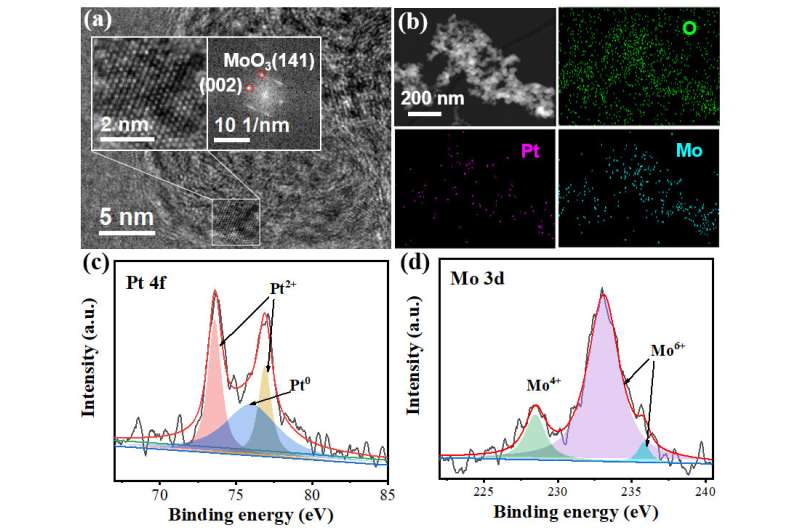
HRTEM and elemental mapping results of Pt-MoO3/C. Credit: Wang Jialu
Researchers from the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported a carbon-supported, Pt-modified MoO3 nanoparticle catalyst for electrochemically selective C=O hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde to produce cinnamyl alcohol.
Their findings were published in Chemical communication.
Cinnamaldehyde (CAL), a representative chemical for α,β-unsaturated aromatic aldehydes, is widely used in hydrogenation reactions to produce high value-added products, among which cinnamyl alcohol (COL) is commonly applied as flavor additive and pharmaceutical raw material.
In this work, the researchers synthesized Pt-modified MoO3 ultrafine particles loaded on activated carbon (Pt-MoO3/C). Electrochemical characterization results showed the apparent reduction peak after the introduction of CAL, and the strong adsorption of CAL on the electrode surface led to a concentration increase in the negative shift of the reduction peak.
As an electrocatalyst, Pt-MoO3/C showed superior electrocatalytic hydrogenation activity over CAL to COL with a high conversion of 99% and selectivity of 78% at -0.4 V, and the Faraday efficiency could reach 50% when doubling the Faraday equivalents of the applied electrical quantity.
The calculation results indicated that the high selectivity to COL was due to the synergistic effect of the Pt and Mo species, which could selectively adsorb the C=O bond of the CAL molecule via vertical adsorption configuration, thereby increasing the CAL hydrogenation selectivity for the generation of COL was improved.
Researchers develop non-precious alloy catalyst for cinnamaldehyde
Jialu Wang et al, Pt-modified MoO3 catalyst for the electrochemically selective C=O hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde, Chemical communication (2022). DOI: 10.1039/D2CC01527G
Quote: New Catalyst for Electrochemically Selective C=O Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde (2022, July 18) Retrieved July 18, 2022 from https://phys.org/news/2022-07-catalyst-electrochemically-hydrogenation-cinnamaldehyde.html
This document is copyrighted. Other than fair dealing for personal study or research, nothing may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.